| .. | ||
| __jest__ | ||
| __mocks__ | ||
| assets | ||
| bin | ||
| flow-typed | ||
| src | ||
| webpack | ||
| .babelrc | ||
| .flowconfig | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .npmignore | ||
| package-lock.json | ||
| package.json | ||
| README.md | ||
inso
A CLI to accompany Insomnia Designer
npm i -g insomnia-inso
Data source
inso will first try to find a .insomnia directory in it's working directory. This directory is generated in a git repository when using git sync in Designer. When inso is used in a CI environment, it will always run against the .insomnia directory.
If inso cannot find the .insomnia directory, it will try to run against the Designer app data directory (if found). You can override both the working directory, and the app data directory, using the --working-dir and --app-data-dir global options.
The [identifier] argument
Typically, Insomnia database id's are quite long, for example: wrk_012d4860c7da418a85ffea7406e1292a. When specifying an identifier for inso, similar to Git hashes, you may choose to concatenate and use the first x characters (for example, wrk_012d486 ), which is very likely to be unique. If in the rare chance the short id is not unique against the data, inso will inform as such.
Additionally, if the [identifier] argument is ommitted from the command, inso will search in the database for the information it needs, and prompt the user. Prompts can be disabled with the --ci global option.
Commands
$ inso [global options] [command]
| Global option | Alias | Description |
|---|---|---|
--working-dir <dir> |
-w |
set working directory |
--app-data-dir <dir> |
-a |
set the app data directory |
--ci |
run in CI, disables all prompts | |
--version |
-v |
output the version number |
--help |
-h |
display help for a command |
$ inso generate config [options] [identifier]
Similar to the Kong Kubernetes and Declarative config plugins for Designer, this command can generate configuration from an API specification, using openapi-2-kong.
[identifier]: this can be a document name, id, or a file path relative to the working directory.
| Option | Alias | Description |
|---|---|---|
--type <type> |
-t |
type of configuration to generate, options are kubernetes and declarative (default: declarative ) |
--output <path> |
-o |
save the generated config to a file in the working directory |
Examples
When running in the git-repo directory
inso generate config
inso generate config spc_46c5a4 --type declarative
inso generate config spc_46c5a4 --type declarative > output.yaml
inso generate config "Sample Specification" --output output.yaml
inso generate config "Sample Specification" --type kubernetes
inso generate config spec.yaml --working-dir another/dir
$ inso lint spec [identifier]
Designer has the ability to lint and validate your OpenAPI specification as you write it. This command adds the same functionality to inso , in order to run linting during CI workflows. Lint results will be printed to the console, and inso will exit with an appropriate exit code.
[identifier]: this can be a document name, or id.
Examples
When running in the git-repo directory
inso lint spec
inso lint spec spc_46c5a4
inso lint spec "Sample Specification"
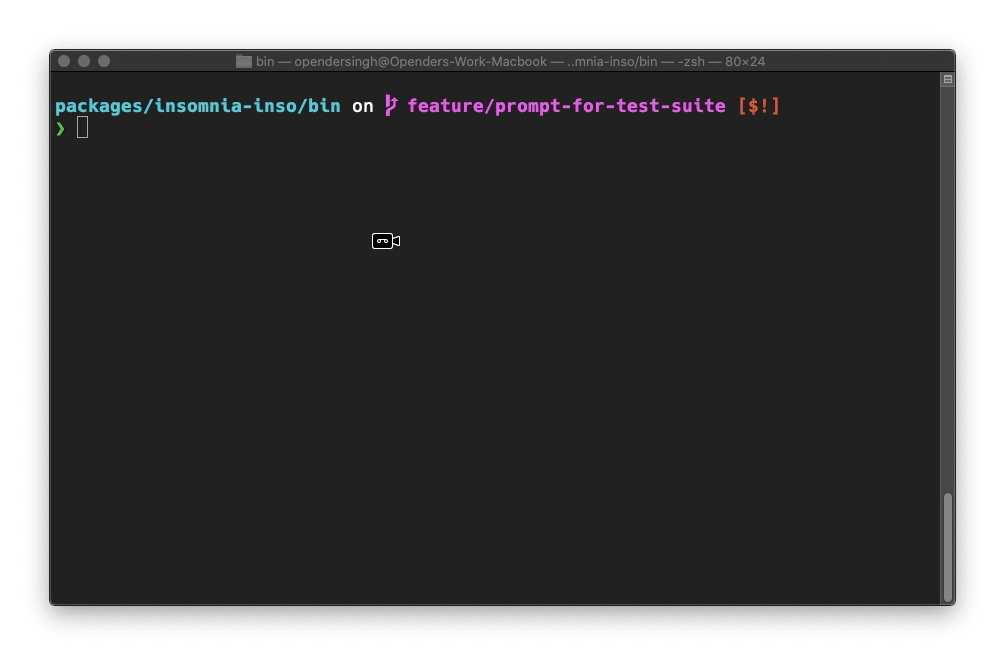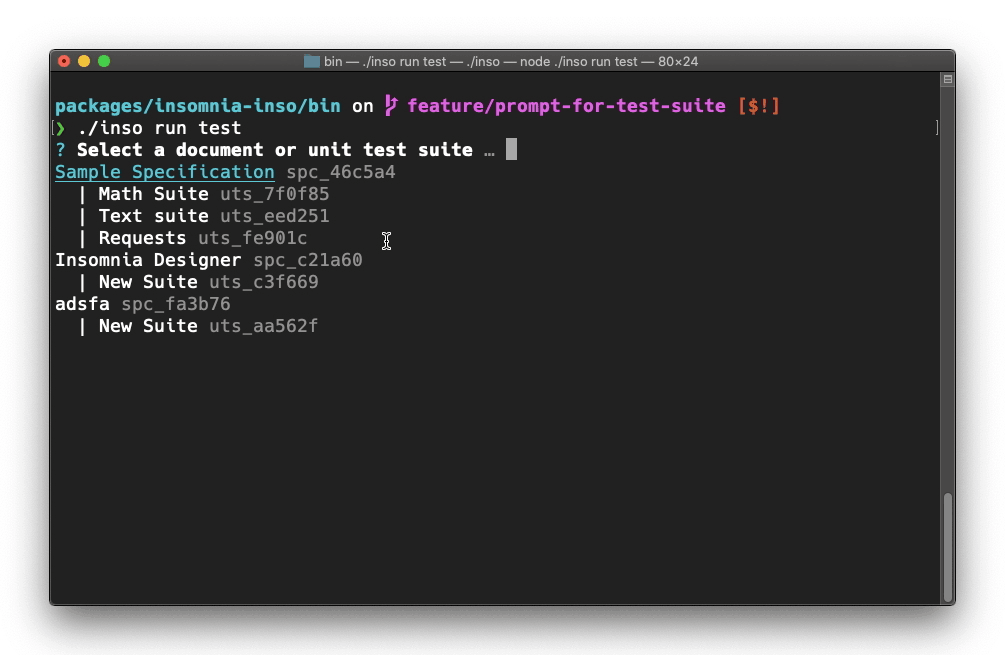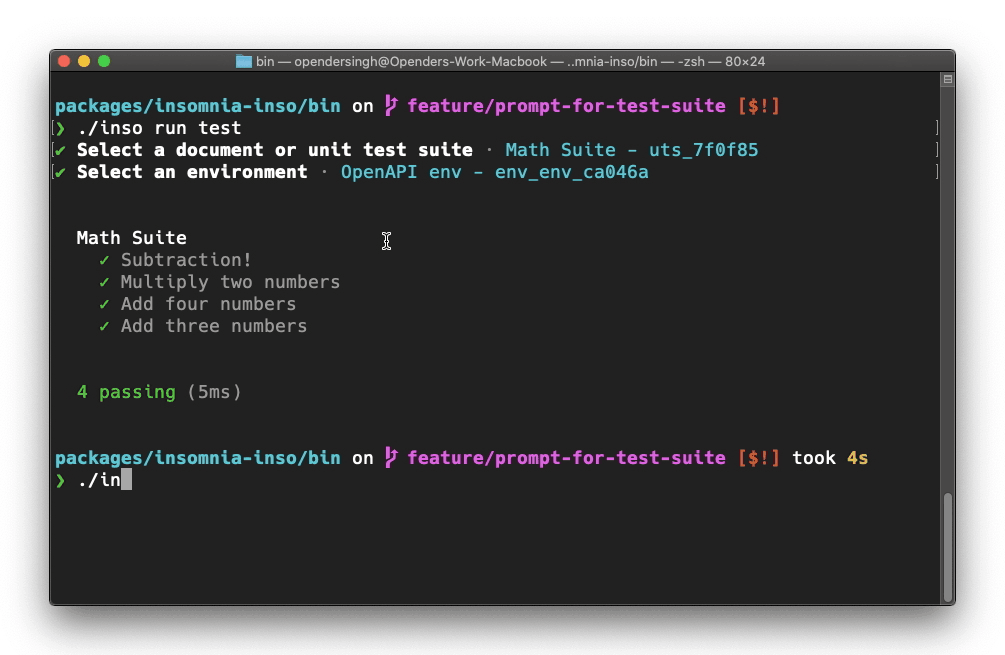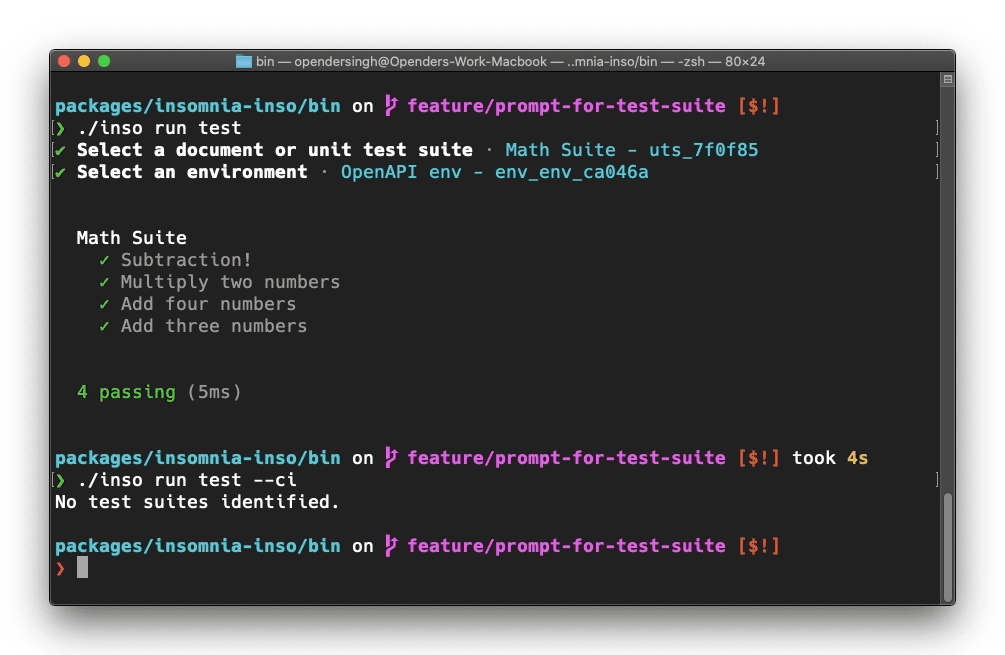
$ inso run test [options] [identifier]
API Unit Testing was introduced with Designer 2020.3.0, and this command adds the functionality to execute those unit tests via the command line, very useful for a CI environment. inso will report on test results, and exit with an appropriate exit code.
[identifier]: this can be the name or id of a workspace, document, or unit test suite.
The test runner is built on top of Mocha, thus many of the options behave as they would in Mocha. The options currently supported are:
| Option | Alias | Description |
|---|---|---|
--env <identifier> |
-e |
the environment to use - an environment name or id |
--reporter <value> |
-r |
reporter to use, options are dot, list, spec, min and progress (default: spec ) |
--test-name-pattern <regex> |
-t |
run tests that match the regex |
--bail |
-b |
abort ("bail") after the first test failure |
--keep-file |
do not delete the generated test file (useful for debugging) |
Examples
When running in the git-repo directory
Not specifying any arguments will prompt
inso run test
Scope by the document name or id
inso run test "Sample Specification" --env "OpenAPI env"
inso run test spc_46c5a4 --env env_env_ca046a
Scope by the a test suite name or id
inso run test "Math Suite" --env "OpenAPI env"
inso run test uts-7f0f85 --env env_env_ca046a
Scope by test name regex, and control test running and reporting
inso run test "Sample Specification" --test-name-pattern Math --env env_env_ca046a
inso run test spc_46c5a4 --reporter progress --bail --keep-file
More examples: #2338.
Continuous Integration
inso has been designed to run in a CI environment, disabling prompts and providing exit codes to pass or fail the CI workflow accordingly. An example workflow run in Github Actions is as follows. This example will checkout > install NodeJS > install inso > run linting > run unit tests > generate configuration. If any of these steps fail, the GH workflow will as well.
# .github/workflows/test.yml
name: Test
jobs:
Linux:
name: Validate API spec
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout branch
uses: actions/checkout@v1
- name: Install NodeJS
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
- name: Install inso
run: npm install -g insomnia-inso
- name: Lint
run: inso lint spec "Designer Demo" --ci
- name: Run test suites
run: inso run test "Designer Demo" --env UnitTest --ci
- name: Generate declarative config
run: inso generate config "Designer Demo" --type declarative --ci
Development
- Bootstrap:
npm run bootstrap - Start the compiler in watch mode:
npm run watch - Run:
./bin/inso -v