# v0.8:Plugin manager & docs
Starting with v0.8, NocoBase begins to provide an available plugin manager and development documentation. Here are the main changes in v0.8.
## Tweaks to the top right corner of the interface
- UI Editor
- Plugin Manager
- Settings Center
- Personal Center
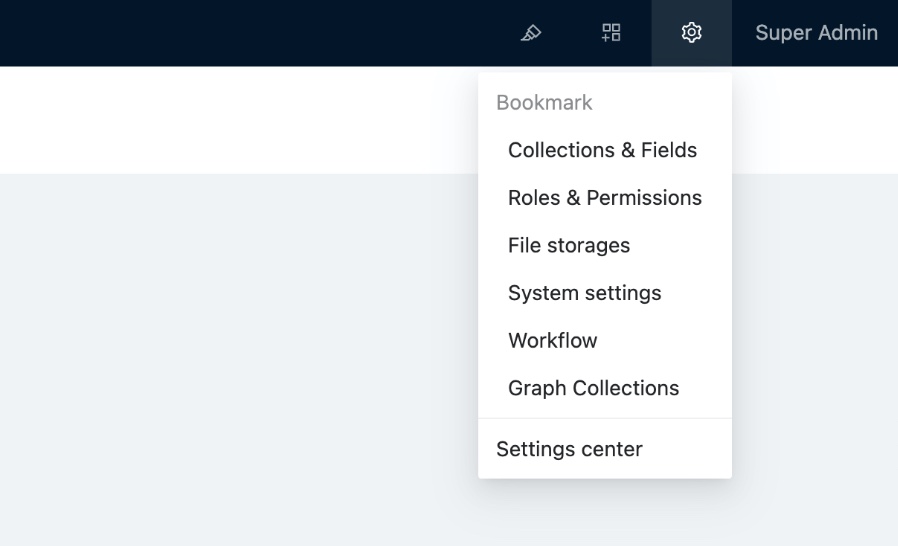 ## The new plugin manager
v0.8 provides a powerful plugin manager for managing plugins in a no-code way.
### Plugin manager flow
## The new plugin manager
v0.8 provides a powerful plugin manager for managing plugins in a no-code way.
### Plugin manager flow
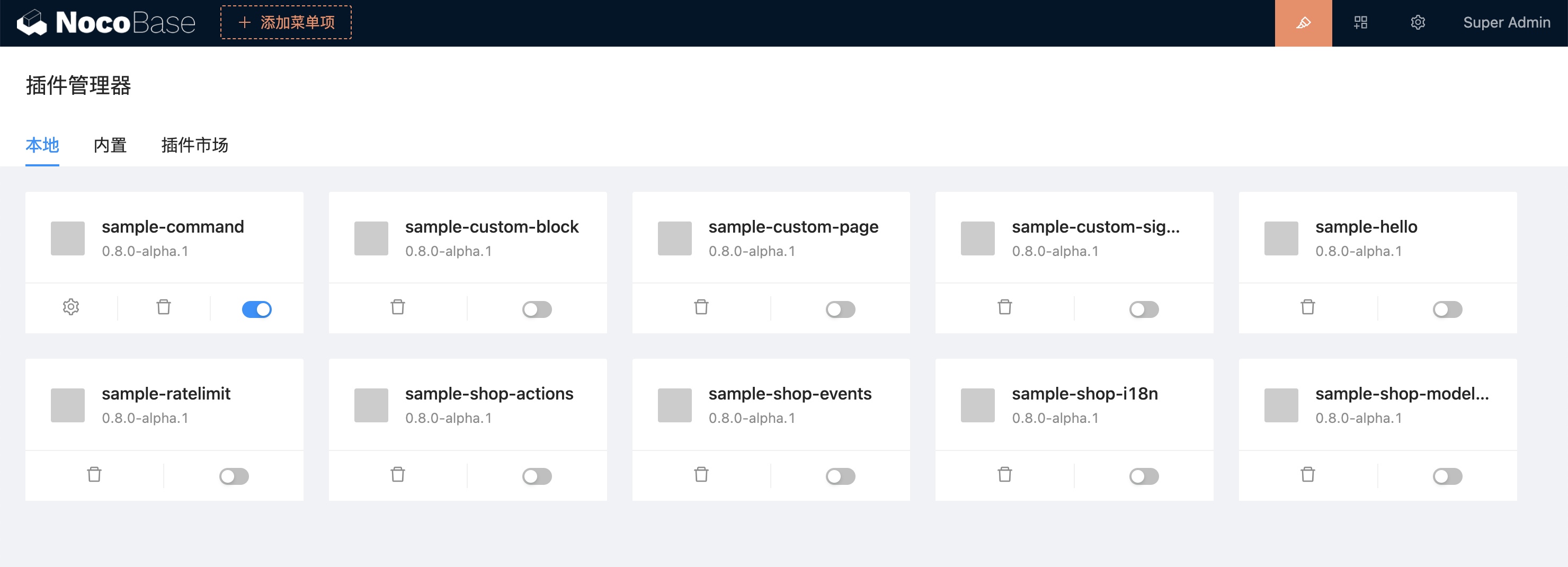
 ### Plugin Manager interface
Currently it is mainly used for disabling, activating and deleting local plugins. Built-in plugins cannot be deleted.
### Plugin Manager interface
Currently it is mainly used for disabling, activating and deleting local plugins. Built-in plugins cannot be deleted.
 ### Plugin Manager command
In addition to being able to activate and disable plugins from the no-code interface, you can also manage plugins more completely from the command line.
```
# Create a plugin
yarn pm create hello
# Register the plugin
yarn pm add hello
# Activate the plugin
yarn pm enable hello
# Disable the plugin
yarn pm disable hello
# Remove the plugin
yarn pm remove hello
```
Note: Releases and upgrades for plugins will be supported in subsequent releases.
```
# Publish the plugin
yarn pm publish hello
# Publish the plugin
yarn pm upgrade hello
```
For more plugin examples, see [packages/samples](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/main/packages/samples).
## Changes of plugin
### Plugin’s directory structure
```
|- /hello
|- /src
|- /client # Plugin client
|- /server # Plugin server
|- client.d.ts
|- client.js
|- package.json # Plugin package information
|- server.d.ts
|- server.js
```
### Plugin’s name specification
NocoBase plugin is also an NPM package, the correspondence rule between plugin name and NPM package name is `${PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX}-${pluginName}`.
`PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX` is the plugin package prefix, which can be customized in .env, [click here for PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX description](https://www.notion.so/api/env#plugin_package_prefix).
For example, a project named `my-nocobase-app` adds the `hello` plugin with package name `@my-nocobase-app/plugin-hello`.
`PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX` is configured as follows.
```
PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX=@nocobase/plugin-,@nocobase/preset-,@my-nocobase-app/plugin-
```
The correspondence between plugin names and package names is
- `users` plugin package name is `@nocobase/plugin-users`
- `nocobase` plugin package name is `@nocobase/preset-nocobase`
- `hello` plugin package named `@my-nocobase-app/plugin-hello`
### Plugin’s lifecycle
v0.8 provides a more complete approach to the plugin lifecycle.
```
import { InstallOptions, Plugin } from '@nocobase/server';
export class HelloPlugin extends Plugin {
afterAdd() {
// After the plugin has been added via pm.add
}
beforeLoad() {
// Before all plugins are loaded, generally used to register classes and event listeners
}
async load() {
// Load configuration
}
async install(options?: InstallOptions) {
// Install logic
}
async afterEnable() {
// After activation
}
async afterDisable() {
// After disable
}
async remove() {
// Remove logic
}
}
export default HelloPlugin;
```
### Front- and back-end entrance for plugins
The lifecycle of the plugin is controlled by the server
```
import { Application } from '@nocobase/server';
const app = new Application({
// ...
});
class MyPlugin extends Plugin {
afterAdd() {}
beforeLoad() {}
load() {}
install() {}
afterEnable() {}
afterDisable() {}
remove() {}
}
app.plugin(MyPlugin, { name: 'my-plugin' });
```
The client side of the plugin exists as Context.Provider (similar to Middleware on the server side)
```
import React from 'react';
import { Application } from '@nocobase/client';
const app = new Application({
apiClient: {
baseURL: process.env.API_BASE_URL,
},
dynamicImport: (name: string) => {
return import(`../plugins/${name}`);
},
});
// When you visit the /hello page, it displays Hello world!
const HelloProvider = React.memo((props) => {
const location = useLocation();
if (location.pathname === '/hello') {
return
### Plugin Manager command
In addition to being able to activate and disable plugins from the no-code interface, you can also manage plugins more completely from the command line.
```
# Create a plugin
yarn pm create hello
# Register the plugin
yarn pm add hello
# Activate the plugin
yarn pm enable hello
# Disable the plugin
yarn pm disable hello
# Remove the plugin
yarn pm remove hello
```
Note: Releases and upgrades for plugins will be supported in subsequent releases.
```
# Publish the plugin
yarn pm publish hello
# Publish the plugin
yarn pm upgrade hello
```
For more plugin examples, see [packages/samples](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/main/packages/samples).
## Changes of plugin
### Plugin’s directory structure
```
|- /hello
|- /src
|- /client # Plugin client
|- /server # Plugin server
|- client.d.ts
|- client.js
|- package.json # Plugin package information
|- server.d.ts
|- server.js
```
### Plugin’s name specification
NocoBase plugin is also an NPM package, the correspondence rule between plugin name and NPM package name is `${PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX}-${pluginName}`.
`PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX` is the plugin package prefix, which can be customized in .env, [click here for PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX description](https://www.notion.so/api/env#plugin_package_prefix).
For example, a project named `my-nocobase-app` adds the `hello` plugin with package name `@my-nocobase-app/plugin-hello`.
`PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX` is configured as follows.
```
PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX=@nocobase/plugin-,@nocobase/preset-,@my-nocobase-app/plugin-
```
The correspondence between plugin names and package names is
- `users` plugin package name is `@nocobase/plugin-users`
- `nocobase` plugin package name is `@nocobase/preset-nocobase`
- `hello` plugin package named `@my-nocobase-app/plugin-hello`
### Plugin’s lifecycle
v0.8 provides a more complete approach to the plugin lifecycle.
```
import { InstallOptions, Plugin } from '@nocobase/server';
export class HelloPlugin extends Plugin {
afterAdd() {
// After the plugin has been added via pm.add
}
beforeLoad() {
// Before all plugins are loaded, generally used to register classes and event listeners
}
async load() {
// Load configuration
}
async install(options?: InstallOptions) {
// Install logic
}
async afterEnable() {
// After activation
}
async afterDisable() {
// After disable
}
async remove() {
// Remove logic
}
}
export default HelloPlugin;
```
### Front- and back-end entrance for plugins
The lifecycle of the plugin is controlled by the server
```
import { Application } from '@nocobase/server';
const app = new Application({
// ...
});
class MyPlugin extends Plugin {
afterAdd() {}
beforeLoad() {}
load() {}
install() {}
afterEnable() {}
afterDisable() {}
remove() {}
}
app.plugin(MyPlugin, { name: 'my-plugin' });
```
The client side of the plugin exists as Context.Provider (similar to Middleware on the server side)
```
import React from 'react';
import { Application } from '@nocobase/client';
const app = new Application({
apiClient: {
baseURL: process.env.API_BASE_URL,
},
dynamicImport: (name: string) => {
return import(`../plugins/${name}`);
},
});
// When you visit the /hello page, it displays Hello world!
const HelloProvider = React.memo((props) => {
const location = useLocation();
if (location.pathname === '/hello') {
return Hello world!
}
return <>{props.children}
});
app.use(HelloProvider);
```
## Custom business code
v0.7 plugins are not complete, custom business code may be scattered in `packages/app/client` and `packages/app/server`, which is not conducive to upgrade and maintenance. v0.8 recommends organizing as a plugin package and using `yarn pm` to manage plugins.
## More complete documentation is provided
- **Welcome**: a quick look at NocoBase
- **Manual**: learn more about the core features provided by the NocoBase platform
- **Plugin Development Tutorial**: Advanced dive into plugin development
- **API Reference**: Check the API usage during plugin development
- **Client Components Library** (in preparation): provides examples and usage of NocoBase components
## More plugin examples are provided
- [command](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/develop/packages/samples/command)
- [custom-block](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/develop/packages/samples/custom-block)
- [custom-page](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/develop/packages/samples/custom-page)
- [custom-signup-page](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/develop/packages/samples/custom-signup-page)
- [hello](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/develop/packages/samples/hello)
- [ratelimit](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/develop/packages/samples/ratelimit)
- [shop-actions](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/develop/packages/samples/shop-actions)
- [shop-events](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/develop/packages/samples/shop-events)
- [shop-i18n](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/develop/packages/samples/shop-i18n)
- [shop-modeling](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/develop/packages/samples/shop-modeling)
## Other new features and functionality
- Import from Excel
- Bulk Update & Edit
- Graphical collection
- Workflow support for viewing execution history
- JSON field
 ## The new plugin manager
v0.8 provides a powerful plugin manager for managing plugins in a no-code way.
### Plugin manager flow
## The new plugin manager
v0.8 provides a powerful plugin manager for managing plugins in a no-code way.
### Plugin manager flow
 ### Plugin Manager command
In addition to being able to activate and disable plugins from the no-code interface, you can also manage plugins more completely from the command line.
```
# Create a plugin
yarn pm create hello
# Register the plugin
yarn pm add hello
# Activate the plugin
yarn pm enable hello
# Disable the plugin
yarn pm disable hello
# Remove the plugin
yarn pm remove hello
```
Note: Releases and upgrades for plugins will be supported in subsequent releases.
```
# Publish the plugin
yarn pm publish hello
# Publish the plugin
yarn pm upgrade hello
```
For more plugin examples, see [packages/samples](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/main/packages/samples).
## Changes of plugin
### Plugin’s directory structure
```
|- /hello
|- /src
|- /client # Plugin client
|- /server # Plugin server
|- client.d.ts
|- client.js
|- package.json # Plugin package information
|- server.d.ts
|- server.js
```
### Plugin’s name specification
NocoBase plugin is also an NPM package, the correspondence rule between plugin name and NPM package name is `${PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX}-${pluginName}`.
`PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX` is the plugin package prefix, which can be customized in .env, [click here for PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX description](https://www.notion.so/api/env#plugin_package_prefix).
For example, a project named `my-nocobase-app` adds the `hello` plugin with package name `@my-nocobase-app/plugin-hello`.
`PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX` is configured as follows.
```
PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX=@nocobase/plugin-,@nocobase/preset-,@my-nocobase-app/plugin-
```
The correspondence between plugin names and package names is
- `users` plugin package name is `@nocobase/plugin-users`
- `nocobase` plugin package name is `@nocobase/preset-nocobase`
- `hello` plugin package named `@my-nocobase-app/plugin-hello`
### Plugin’s lifecycle
v0.8 provides a more complete approach to the plugin lifecycle.
```
import { InstallOptions, Plugin } from '@nocobase/server';
export class HelloPlugin extends Plugin {
afterAdd() {
// After the plugin has been added via pm.add
}
beforeLoad() {
// Before all plugins are loaded, generally used to register classes and event listeners
}
async load() {
// Load configuration
}
async install(options?: InstallOptions) {
// Install logic
}
async afterEnable() {
// After activation
}
async afterDisable() {
// After disable
}
async remove() {
// Remove logic
}
}
export default HelloPlugin;
```
### Front- and back-end entrance for plugins
The lifecycle of the plugin is controlled by the server
```
import { Application } from '@nocobase/server';
const app = new Application({
// ...
});
class MyPlugin extends Plugin {
afterAdd() {}
beforeLoad() {}
load() {}
install() {}
afterEnable() {}
afterDisable() {}
remove() {}
}
app.plugin(MyPlugin, { name: 'my-plugin' });
```
The client side of the plugin exists as Context.Provider (similar to Middleware on the server side)
```
import React from 'react';
import { Application } from '@nocobase/client';
const app = new Application({
apiClient: {
baseURL: process.env.API_BASE_URL,
},
dynamicImport: (name: string) => {
return import(`../plugins/${name}`);
},
});
// When you visit the /hello page, it displays Hello world!
const HelloProvider = React.memo((props) => {
const location = useLocation();
if (location.pathname === '/hello') {
return
### Plugin Manager command
In addition to being able to activate and disable plugins from the no-code interface, you can also manage plugins more completely from the command line.
```
# Create a plugin
yarn pm create hello
# Register the plugin
yarn pm add hello
# Activate the plugin
yarn pm enable hello
# Disable the plugin
yarn pm disable hello
# Remove the plugin
yarn pm remove hello
```
Note: Releases and upgrades for plugins will be supported in subsequent releases.
```
# Publish the plugin
yarn pm publish hello
# Publish the plugin
yarn pm upgrade hello
```
For more plugin examples, see [packages/samples](https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/main/packages/samples).
## Changes of plugin
### Plugin’s directory structure
```
|- /hello
|- /src
|- /client # Plugin client
|- /server # Plugin server
|- client.d.ts
|- client.js
|- package.json # Plugin package information
|- server.d.ts
|- server.js
```
### Plugin’s name specification
NocoBase plugin is also an NPM package, the correspondence rule between plugin name and NPM package name is `${PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX}-${pluginName}`.
`PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX` is the plugin package prefix, which can be customized in .env, [click here for PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX description](https://www.notion.so/api/env#plugin_package_prefix).
For example, a project named `my-nocobase-app` adds the `hello` plugin with package name `@my-nocobase-app/plugin-hello`.
`PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX` is configured as follows.
```
PLUGIN_PACKAGE_PREFIX=@nocobase/plugin-,@nocobase/preset-,@my-nocobase-app/plugin-
```
The correspondence between plugin names and package names is
- `users` plugin package name is `@nocobase/plugin-users`
- `nocobase` plugin package name is `@nocobase/preset-nocobase`
- `hello` plugin package named `@my-nocobase-app/plugin-hello`
### Plugin’s lifecycle
v0.8 provides a more complete approach to the plugin lifecycle.
```
import { InstallOptions, Plugin } from '@nocobase/server';
export class HelloPlugin extends Plugin {
afterAdd() {
// After the plugin has been added via pm.add
}
beforeLoad() {
// Before all plugins are loaded, generally used to register classes and event listeners
}
async load() {
// Load configuration
}
async install(options?: InstallOptions) {
// Install logic
}
async afterEnable() {
// After activation
}
async afterDisable() {
// After disable
}
async remove() {
// Remove logic
}
}
export default HelloPlugin;
```
### Front- and back-end entrance for plugins
The lifecycle of the plugin is controlled by the server
```
import { Application } from '@nocobase/server';
const app = new Application({
// ...
});
class MyPlugin extends Plugin {
afterAdd() {}
beforeLoad() {}
load() {}
install() {}
afterEnable() {}
afterDisable() {}
remove() {}
}
app.plugin(MyPlugin, { name: 'my-plugin' });
```
The client side of the plugin exists as Context.Provider (similar to Middleware on the server side)
```
import React from 'react';
import { Application } from '@nocobase/client';
const app = new Application({
apiClient: {
baseURL: process.env.API_BASE_URL,
},
dynamicImport: (name: string) => {
return import(`../plugins/${name}`);
},
});
// When you visit the /hello page, it displays Hello world!
const HelloProvider = React.memo((props) => {
const location = useLocation();
if (location.pathname === '/hello') {
return