* makes this `yaml` import match all others for better or for worse, until we upgrade `YAML` (it's now written in TypeScript) we should probably aim for consistency. * adds overloads so that types of package exports it would be FAR preferable to use an object with the arguments instead because then we don't have to fall into all the traps that come with overloads, but I am avoiding changing the actual call signature of these function. * fixes and updates types * corrects mispelling * removes shim types and exports actual types from openapi-2-kong we had everything in place for the rest of the build pipeline to consume these types, but were missing the main exports at the root index.ts file * use actual openapi-2-kong types now that they're available * use existing variable for filePath * extracts o2k-specific helper data to live in o2k evidently, this data is useful for the usage of o2k, therefore o2k should be the thing exporting it. * use KubernetesManifest for name of kubernetes manifest union when first naming this, I didn't have much more context than the property name (documents), so after taking a look, it's clear that these are kubernetes manifests * removes attempt at correctly typing overloads I will return to this, and so I'm leaving it here in a commit rather than squashing it out, but I can't see a way to get it to work without changing the signature in a big way. * fixes error (now that there are yaml types) * makes `K8s` vs `Kubernetes` type terminology consistent part of the motivation for this is that there are significant things in common between the two kinds of configs, making them closer in form is therefore ideal. * updates mistake in name per review feedback |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| assets | ||
| bin | ||
| src | ||
| webpack | ||
| .eslintignore | ||
| .eslintrc.js | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .npmignore | ||
| jest.config.js | ||
| package-lock.json | ||
| package.json | ||
| README.md | ||
| tsconfig.build.json | ||
| tsconfig.json | ||
Table of Contents
- Data source
- The
[identifier]argument - Global options
- Commands
- Configuration
- Git Bash
- Continuous Integration
- Development
Data source
inso will first try to find a .insomnia directory in it's working directory. This directory is generated in a git repository when using git sync in Designer. When inso is used in a CI environment, it will always run against the .insomnia directory.
If inso cannot find the .insomnia directory, it will try to run against the Designer app data directory (if found). You can override both the working directory, and the app data directory, using the --workingDir and --appDataDir global options.
The [identifier] argument
Typically, Insomnia database id's are quite long, for example: wrk_012d4860c7da418a85ffea7406e1292a . When specifying an identifier for inso , similar to Git hashes, you may choose to concatenate and use the first x characters (for example, wrk_012d486 ), which is very likely to be unique. If in the rare chance the short id is not unique against the data, inso will inform as such.
Additionally, if the [identifier] argument is ommitted from the command, inso will search in the database for the information it needs, and prompt the user. Prompts can be disabled with the --ci global option.
Global options
$ inso [global options] [command]
| Global option | Alias | Description |
|---|---|---|
--workingDir <dir> |
-w |
set working directory |
--appDataDir <dir> |
-a |
set the app data directory |
--config <path> |
path to the configuration file | |
--ci |
run in CI, disables all prompts | |
--verbose |
show additional logs while running a command | |
--printOptions |
print the loaded options | |
--version |
-v |
output the version number |
--help |
-h |
display help for a command |
Commands
$ inso generate config [identifier]
Similar to the Kong Kubernetes and Declarative config plugins for Designer, this command can generate configuration from an API specification, using openapi-2-kong.
[identifier]: this can be a document name, id, or a file path relative to the working directory.
| Option | Alias | Description |
|---|---|---|
--type <type> |
-t |
type of configuration to generate, options are kubernetes and declarative (default: declarative ) |
--output <path> |
-o |
save the generated config to a file in the working directory |
--tags <tags> |
comma separated list of tags to apply to each entity |
Examples
When running in the git-repo directory
Not specifying any arguments will prompt
inso generate config
Scope by the document name or id
inso generate config spc_46c5a4 --type declarative
inso generate config "Sample Specification" --type kubernetes
Scope by a file on the filesystem
inso generate config spec.yaml
inso generate config spec.yaml --workingDir another/dir
Add tags
inso generate config spec.yaml --tags first
inso generate config spec.yaml --tags "first,second"
Output to file
inso generate config spc_46c5a4 --output output.yaml
inso generate config spc_46c5a4 > output.yaml
$ inso lint spec [identifier]
Designer has the ability to lint and validate your OpenAPI specification as you write it. This command adds the same functionality to inso , in order to run linting during CI workflows. Lint results will be printed to the console, and inso will exit with an appropriate exit code.
[identifier]: this can be a document name, or id.
Examples
When running in the git-repo directory
Not specifying any arguments will prompt
inso lint spec
Scope by the document name or id
inso lint spec spc_46c5a4
inso lint spec "Sample Specification"
$ inso run test [identifier]
API Unit Testing was introduced with Designer 2020.3.0, and this command adds the functionality to execute those unit tests via the command line, very useful for a CI environment. inso will report on test results, and exit with an appropriate exit code.
[identifier]: this can be the name or id of a workspace, document, or unit test suite.
The test runner is built on top of Mocha, thus many of the options behave as they would in Mocha. The options currently supported are:
| Option | Alias | Description |
|---|---|---|
--env <identifier> |
-e |
the environment to use - an environment name or id |
--reporter <value> |
-r |
reporter to use, options are dot, list, min, progress, spec (default: spec ) |
--testNamePattern <regex> |
-t |
run tests that match the regex |
--bail |
-b |
abort ("bail") after the first test failure |
--keepFile |
do not delete the generated test file (useful for debugging) |
Examples
When running in the git-repo directory
Not specifying any arguments will prompt
inso run test
Scope by the document name or id
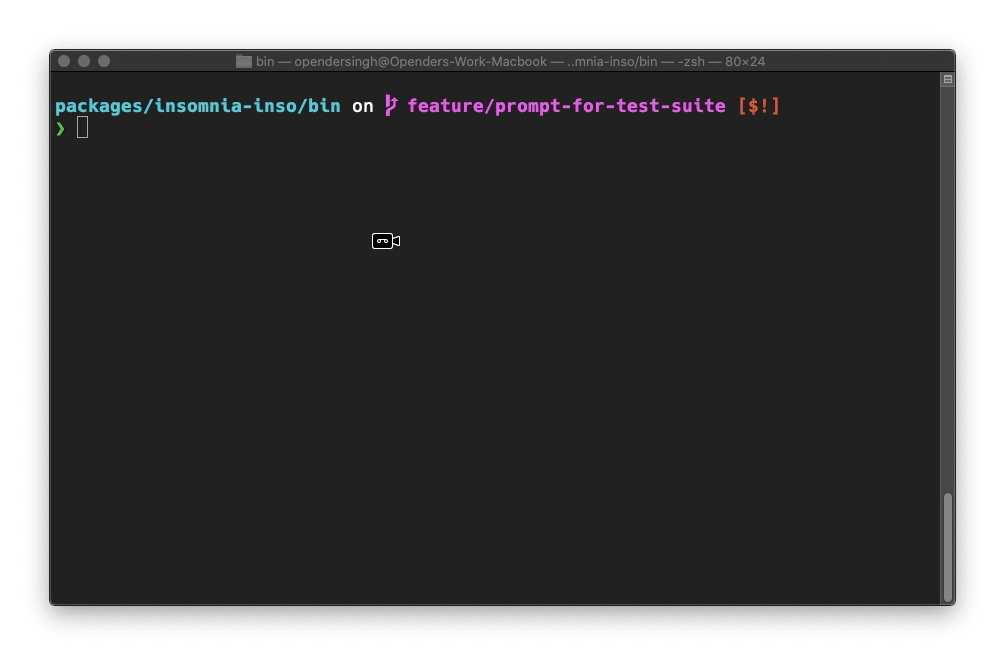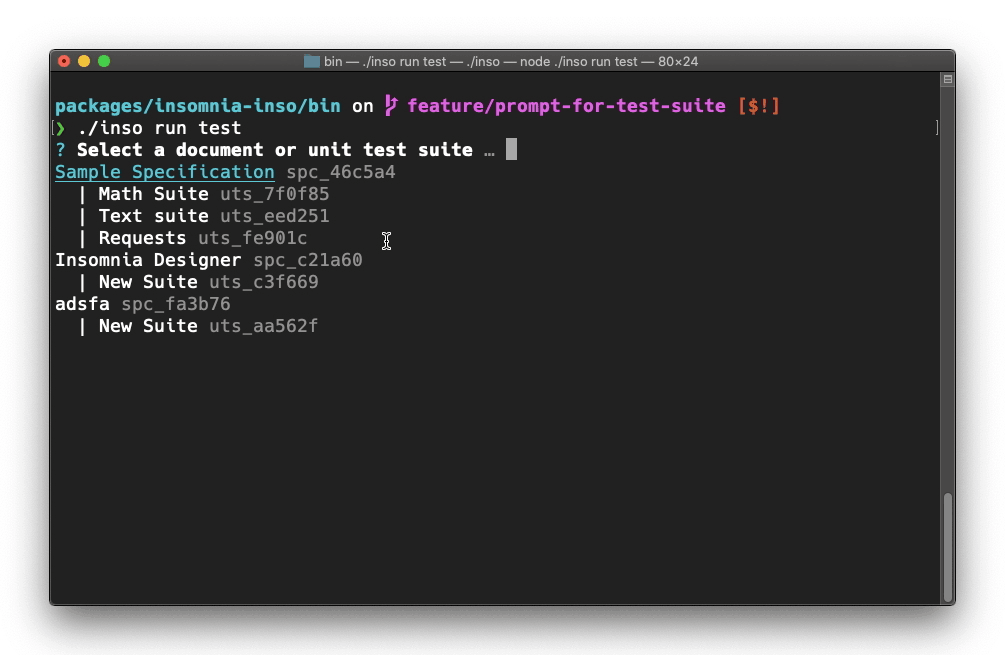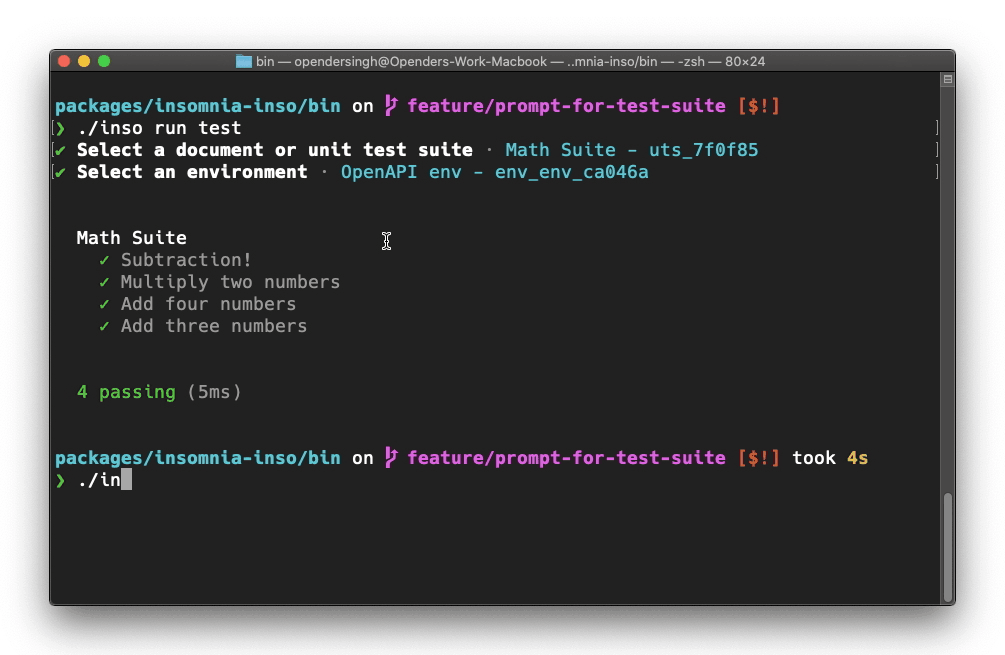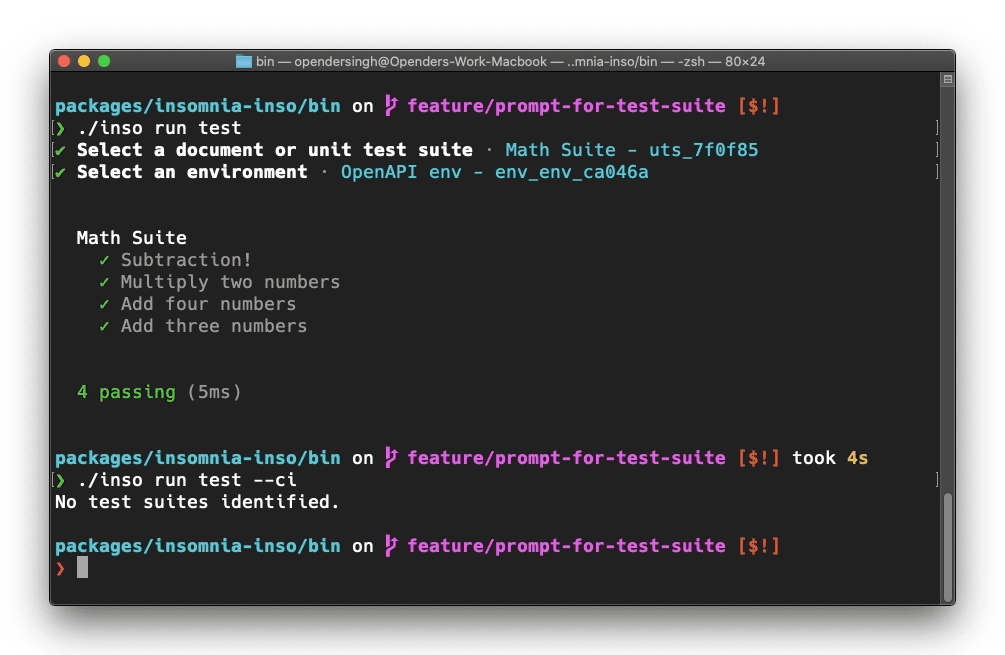
inso run test "Sample Specification" --env "OpenAPI env"
inso run test spc_46c5a4 --env env_env_ca046a
Scope by the a test suite name or id
inso run test "Math Suite" --env "OpenAPI env"
inso run test uts-7f0f85 --env env_env_ca046a
Scope by test name regex, and control test running and reporting
inso run test "Sample Specification" --testNamePattern Math --env env_env_ca046a
inso run test spc_46c5a4 --reporter progress --bail --keepFile
More examples: #2338.
$ inso export spec [identifier]
This command will extract and export the raw OpenAPI specification from the data store. If the --output option is not specified, the spec will print to console.
[identifier]: this can be a document name, or id.
| Option | Alias | Description |
|---|---|---|
--output <path> |
-o |
save the generated config to a file in the working directory |
Examples
When running in the git-repo directory
Not specifying any arguments will prompt
inso export spec
Scope by the document name or id
inso export spec spc_46c5a4
inso export spec "Sample Specification"
Output to file
inso export spec spc_46c5a4 --output output.yaml
inso export spec spc_46c5a4 > output.yaml
$ inso script <name>
The inso config file supports scripts, akin to NPM scripts defined in a package.json file. These scripts can be executed by inso by running inso script <name> , or simply inso <name> as this is the default command. Any options passed to this command, will be forwarded to the script being executed.
Examples
When running in the git-repo directory, with the following inso config file.
# .insorc.yaml
scripts:
lint: lint spec "Sample Specification"
gen-conf: generate config "Sample Specification"
gen-conf:k8s: gen-conf --type kubernetes
Run commands with or without the script prefix
inso script gen-conf
inso gen-conf
If a conflict exists with another command (eg. lint ), you must prefix with script
inso script lint
inso lint # will not work
Any options passed during script invocation will be forwarded to the script
inso gen-conf # generates declarative config (default)
inso gen-conf:k8s # generates kubernetes config
inso gen-conf:k8s -t declarative # generates declarative config
inso gen-conf:k8s -o output.yaml # generates kubernetes config to output.yaml
Configuration
Inso can be configured with a configuration file, allowing you to specify options and scripts. For example, when running in a CI environment, you may choose to specify the steps as scripts in a config file, so that the same commands can be run both locally and in CI.
Inso uses cosmiconfig for config file management, meaning any of the following items found in the working tree are automatically used:
insoproperty inpackage.json.insorcfile in JSON or YAML format.insorc.jsonfile.insorc.yaml,.insorc.yml, or.insorc.jsfileinso.config.jsfile exporting a JS object
Alternatively, you can use the --config <file> global option to specify an exact file to use, if it exists outside the directory tree.
Options
Options from the config file are combined with option defaults and any explicit overrides specified in script or command invocations. This combination is in priority order: command options > config file options > default options.
Any options specified in this file will apply to all scripts and manual commands. You can override these options by specifying them explicitly, when invoking a script or command.
Only global options can be set in the config file.
Scripts
Scripts can have any name, and can be nested. Scripts must be prefixed with inso (see example below). Each command behaves the same way, as described in the sections above.
Example
# .insorc.yaml
options:
ci: false
scripts:
test-spec: inso run test Demo --env DemoEnv --reporter progress
test-spec:200s: inso testSpec --testNamePattern 200
test-spec:404s: inso testSpec --testNamePattern 404
test-math-suites: inso run test uts_8783c30a24b24e9a851d96cce48bd1f2 --env DemoEnv
test-request-suite: inso run test uts_bce4af --env DemoEnv --bail
lint: inso lint spec Demo # must be invoked as `inso script lint`
gen-conf: inso generate config "Designer Demo" --type declarative
gen-conf:k8s: inso gen-conf --type kubernetes
Git Bash
Git Bash on Windows is not interactive and therefore prompts from inso will not work as expected. You may choose to specify the identifiers for each command explicitly, or run inso using winpty :
winpty inso.cmd generate config
Continuous Integration
inso has been designed to run in a CI environment, disabling prompts and providing exit codes to pass or fail the CI workflow accordingly. An example workflow run in Github Actions is as follows. This example will checkout > install NodeJS > install inso > run linting > run unit tests > generate configuration. If any of these steps fail, the GH workflow will as well.
# .github/workflows/test.yml
name: Test
jobs:
Linux:
name: Validate API spec
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout branch
uses: actions/checkout@v1
- name: Install NodeJS
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
- name: Install inso
run: npm install --global insomnia-inso
- name: Lint
run: inso lint spec "Designer Demo" --ci
- name: Run test suites
run: inso run test "Designer Demo" --env UnitTest --ci
- name: Generate declarative config
run: inso generate config "Designer Demo" --type declarative --ci
Development
- Bootstrap:
npm run bootstrap - Start the compiler in watch mode:
npm run start - Run:
./bin/inso -v